In the wake of the Paris Climate Agreement, there is an increasing need to monitor emissions from fossil fuel combustion around the world. For CO2 in particular, satellite imagers are being designed to observe the emission plumes from large point sources and intense urban area sources. To assess their potential, researchers in the CoCO2 project have tested a simple emission estimation scheme on the multi-year archive of the two NASA Orbiting Carbon Observatories (OCO-2 and OCO-3), which provide dense observations along the orbit line, but with a narrow swath.
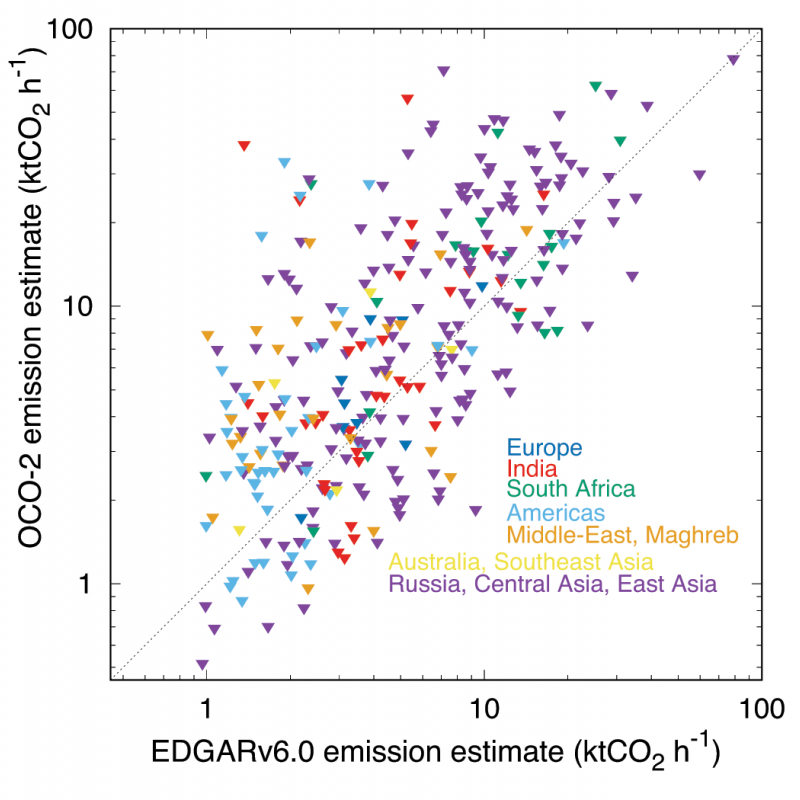
Results have been compared with a global gridded and hourly emission inventory (EDGARv6.0). The corresponding emission estimates explain a large part of the inventory variability, despite uncertainty in both datasets (see figure). Consistent variations in the middle emission values are seen at different time scales. These results suggest that the differences between the satellite-based inverse model estimates and the inventory estimates are mostly random. This implies that trends can be calculated robustly in areas of favourable observation conditions, especially when future satellite CO2 imagers provide an order of magnitude more data. Details of the study can be found in an article that was just published in Geophysical Research Letters.